2. 中英环境科学研究中心, 华南农业大学, 广州 510642
2. Joint Institute for Environmental Research & Education, LEC-SCAU-GIG, Guangzhou 510642, China
当前世界各国对土壤污染修复技术均进行了广泛的研究,但与欧美等发达国家相比,我国土地污染研究起步较晚,且一般为单一的物理、化学与工程方法,缺乏基于不同风险等级的控制技术、分级管理和治理体系,难以应对污染日益严重的不利局面,不足以支撑农产品安全生产和产地环境可持续发展的现实需求,难以成为保障农田农产品安全生产的主导技术,而且大部分研究成果尚未进行大规模生产实践。我国地域辽阔,不同地区土壤类型、气候、水文等有较大差异,耕地污染类型多样,生态环境风险不等,因此我国耕地土壤污染防控技术的研究是一项长期、复杂、艰巨且极其迫切的任务。
由于土壤环境的复杂性,用原有的物理、化学、植物及微生物等单一的方法对复合污染进行修复,都很难达到较好的效果,因此需要将各种单项修复技术进行合理的集成,形成污染耕地过程控制技术体系。耕地土壤修复技术的集成需要基于不同风险等级的控制技术,综合考虑各个单项技术的特点、资金投入、分级管理和治理模式。根据不同地区农业资源实际问题,针对不同类型农田污染开展安全利用技术研究,形成相应的技术体系与模式,使这部分耕地的持续安全利用成为可能,是应对人口迅速增长、耕地面积减少、环境日趋恶化局面的必然选择,其生态效益、环境效益和社会效益将十分巨大。
1 适用于耕地土壤修复的单项技术入库重金属污染耕地修复的技术集成首先需要对现有的、适用于农田土壤修复的单项技术进行总结、归纳和入库。我们选取了植物修复技术、农艺修复技术、间套种技术、土壤淋洗技术和土壤钝化技术等几大类技术,通过国内外文献调研、相关国家环境保护部门门户网站查阅以及专家咨询、研讨等方式,系统收集和整理现行的耕地土壤修复技术进行入库。根据现有的各项重金属单项控制技术的研究及工程应用案例,我们凝练出适用于农田土壤修复的单项技术推荐及其相应的技术特性,具体如表 1~表 6。
|
|
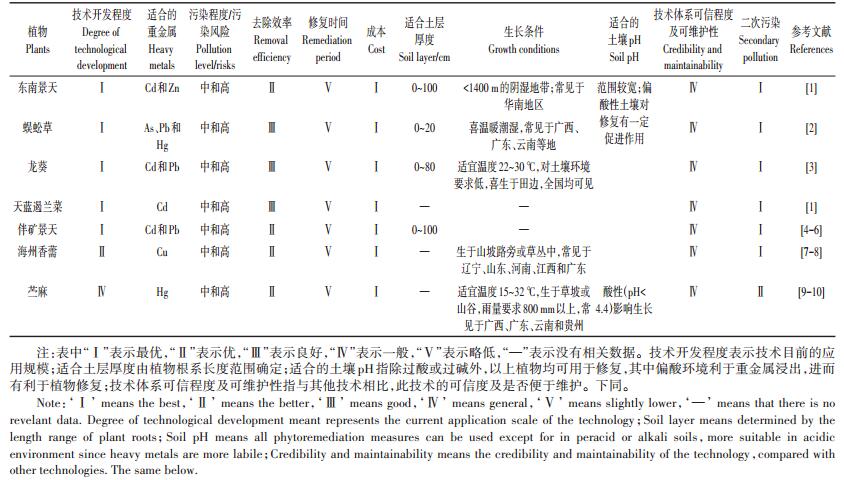
表 1 植物修复技术推荐及技术特性 Table 1 Recommendation and technical characteristics of phytoremediation technology |
|
|
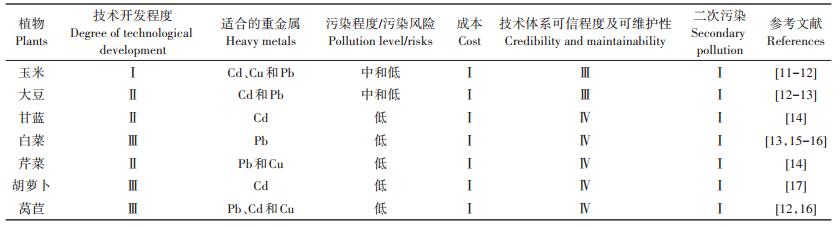
表 2 低累积作物技术推荐及其技术特性 Table 2 Recommendation and technical characteristics of low accumulation crop technology |
|
|
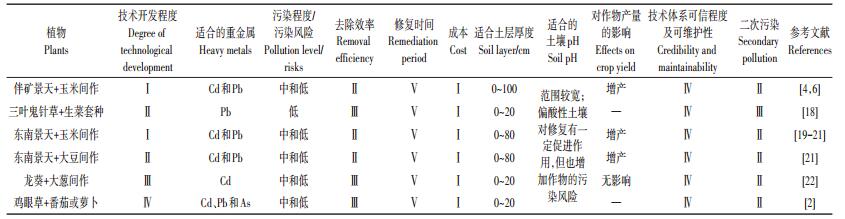
表 3 间作套种技术推荐及其技术特性 Table 3 Recommendation and technical characteristics of intercropping technology |
|
|
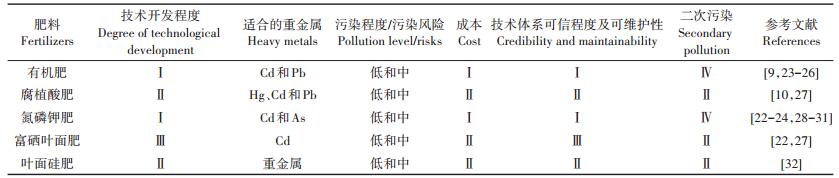
表 4 水肥管理技术推荐及技术特性 Table 4 Recommendation and technical characteristics of water and fertilizer management technology |
|
|
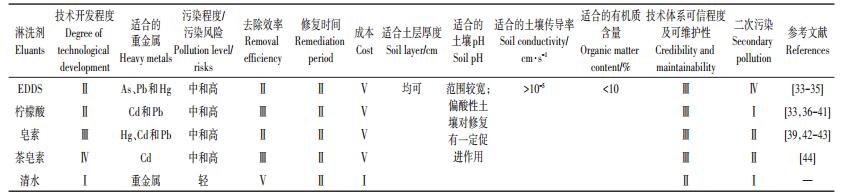
表 5 土壤淋洗技术推荐及技术特性 Table 5 Recommendation and technical characteristics of soil leaching technology |
|
|
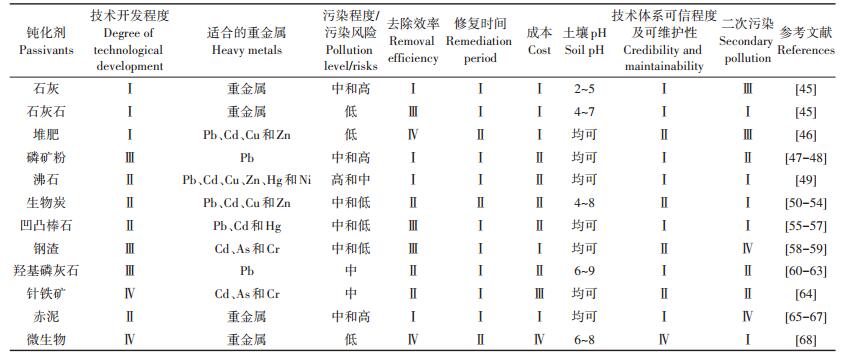
表 6 钝化技术推荐与技术特征 Table 6 Recommendation and technical characteristics of immobilization technology |
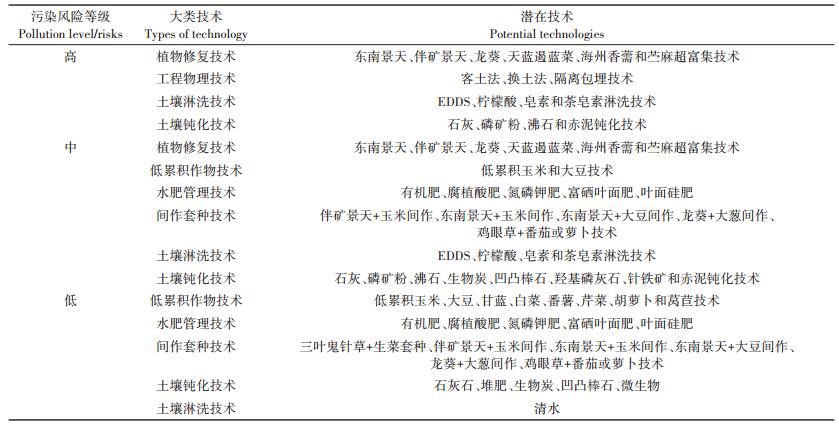
现阶段污染修复项目资金投入较大,试验技术繁杂,鉴于有些技术的投资与运行参数不完整、实际应用时间不长、推广价值有待检验等原因,试点选取的技术可偏向于植物修复、微生物修复、电化学修复等原位修复技术。经济条件宽裕的省区,可因地制宜地开展各类修复技术的试点示范。表 7归纳了适用于不同污染风险等级农田土壤的修复治理技术。
|
|
表 7 不同污染风险等级农田土壤修复治理技术汇总 Table 7 Summary of soil remediation techniques for farmland of different pollution risk levels |
依据农田污染的生态净化功能与机制建立农田污染的分级分类管控技术模式具有重要意义。根据污染源和污染物情况,确定污染农田风险等级,基于各项单项过程控制技术进行不同风险等级耕地过程控制技术的组合集成,针对不同风险等级的污染耕地需要因地制宜地选取合适的过程控制组合技术体系。耕地土壤污染的风险管控模式和技术集成体系的选择需要考虑污染风险等级、污染源、污染途径、污染土壤特性、单项技术体系特性五个影响因素。在修复技术的选择上需要确保污染农田的修复效果以及农田安全利用和风险控制的要求,优先选择能够降低污染物毒性、迁移性和含量的技术。
在选取的单项过程控制技术入库后,需要建立单项过程控制技术的筛选机制。根据耕地污染风险等级,结合影响区域耕地土壤环境质量的因素,并考虑耕地土壤污染修复的单项过程控制技术主要受土壤特性、单项技术的适用性等方面因素的影响。在两个影响因素中选取特征因子如土壤pH、土壤机械组成等,开展典型案例分析、专家经验论证,将各个单项过程控制技术的特点与特征因子对应。构建单项过程控制修复技术体系中单项技术的筛选机制,以为后续土壤环境保护和综合管控模式和技术集成体系做基石铺垫。
技术选取的基本原则是:(1)短期效果;(2)长期效果;(3)对污染物毒性、迁移性和数量减少的程度;(4)可操作性;(5)成本;(6)符合应用与其他相关要求;(7)全面保护人体健康与环境;(8)政府的接受程度;(9)公众接受程度。
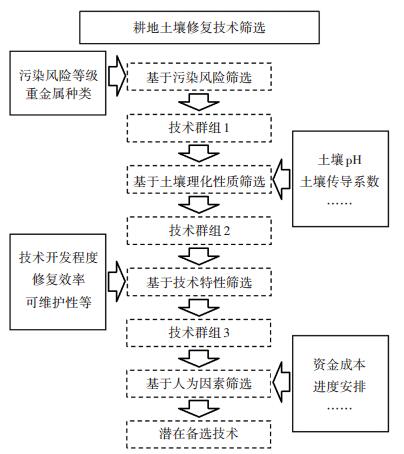
上述内容中推荐了一些可行的技术,而技术的选择需要结合具体的农田土壤环境质量特征来进行。因此,重金属污染农田土壤修复技术的筛选步骤应如图 1进行。
|
图 1 重金属污染农田土壤修复技术的筛选步骤 Figure 1 Screening steps of remediation techniques for heavy metal contaminated farmland soils |
(1)基于污染风险筛选:根据第2部分提到的待修复农田土壤环境质量调查,提取出污染农田土壤污染风险等级和重金属等信息,在表 1~表 5中初步筛选出符合污染等级和重金属类型的技术群1。
(2)基于土壤理化性质筛选:在技术群1中,按照技术开展所对应的农田土壤相关性质指标(如土壤pH、土壤传导系数、土壤污染的深度等),筛选出技术群2。
(3)基于技术特性筛选:在技术群2中,依据小类技术的技术特性(如开发程度、可维护性、修复效率等),筛选出技术群3。
(4)基于人为因素筛选:在技术群3中,按照修复过程进度安排、资金成本等因素,筛选出技术群4,即潜在备选技术,相关人员可在本技术群中选出合适的技术。若技术群4中包含两种以上的技术,则需要进一步开展实验论证。
4 重金属污染农田集成修复技术展望综上可知,单项修复治理技术都有各自的技术特点和适用范围,它们在重金属类型相对单一的农田土壤上可以发挥良好的效果。然而,随着工业的不断发展,投入农田中的污染物类型日趋复杂。不同污染源作用下,农田土壤中重金属的类型、浓度和价态均有差异。因此,很难仅靠单项技术完成大面积的农田修复。在单项技术无法达到修复目标时,应考虑进行有效的技术集成。可根据污染源、污染物类型和浓度,确定农田污染等级,并基于各单项修复治理技术进行合理的技术集成,形成几套针对于不同风险等级的且具有潜在推广价值的组合技术。
| [1] |
何启贤. 镉超富集植物筛选研究进展[J]. 环境保护与循环经济, 2013, 33(1): 46-49. HE Qi-xian. Advances in screening of cadmium hyperaccumulators[J]. Environmental Protection and Circular Economy, 2013, 33(1): 46-49. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-1021.2013.01.016 |
| [2] |
叶文玲, 樊霆, 鲁洪娟, 等. 蜈蚣草的植物修复作用对土壤中砷总量及形态分布的影响研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2014, 45(4): 1003-1007. YE Wen-ling, FAN Ting, LU Hong-juan, et al. The effects of phytoremediation with Pteris vittata on arsenic concentration and morphological distribution in arsenic contaminated soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2014, 45(4): 1003-1007. |
| [3] |
Zou X L. Phytoextraction of heavy metals from contaminated soil by cocropping Solanum nigrum L. with ryegrass associated with endophytic bacterium[J]. Separation Science and Technology, 2015, 50(12): 1806-1813. DOI:10.1080/01496395.2015.1014058 |
| [4] |
Deng L, Li Z, Wang J, et al. Long-term field phytoextraction of zinc/cadmium contaminated soil by Sedum plumbizincicola under different agronomic strategies[J]. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 2016, 18(2): 134-140. DOI:10.1080/15226514.2015.1058328 |
| [5] |
Luo K, Ma T, Liu H, et al. Efficiency of repeated phytoextraction of cadmium and zinc from an agricultural soil contaminated with sewage sludge[J]. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 2015, 17(6): 575-582. DOI:10.1080/15226514.2014.935286 |
| [6] |
赵冰, 沈丽波, 程苗苗, 等. 麦季间作伴矿景天对不同土壤小麦-水稻生长及锌镉吸收性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2011, 22(10): 2725-2731. ZHAO Bing, SHEN Li-bo, CHENG Miao-miao, et al. Effects of intercropping Sedum plumbizincicola in wheat growth season under wheatrice rotation on the crops growth and their heavy metals uptake from different soil types[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2011, 22(10): 2725-2731. |
| [7] |
刘婷婷, 彭程, 王梦, 等. 海州香薷根细胞壁对铜的吸附固定机制研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2014, 34(2): 514-523. LIU Ting-ting, PENG Cheng, WANG Meng, et al. Mechanism of fixation and adsorption of copper on root cell wall of Elsholtzia splendens[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2014, 34(2): 514-523. |
| [8] |
潘澄, 滕应, 骆永明, 等. 紫花苜蓿、海州香薷及伴矿景天对多氯联苯与重金属复合污染土壤的修复作用[J]. 土壤学报, 2012, 49(5): 1062-1067. PAN Cheng, TENG Ying, LUO Yong-ming, et al. Effects of Medicago sativa, Elsholtzia splendens and Sedum plumbizincicola remedying soils contaminated with both polychlorinated biphenyls and heavy metals[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2012, 49(5): 1062-1067. |
| [9] |
马铁铮, 马友华, 付欢欢, 等. 生物有机肥和生物炭对Cd和Pb污染稻田土壤修复的研究[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2015, 32(1): 14-19. MA Tie-zheng, MA You-hua, FU Huan-huan, et al. Remediation of biological organic fertilizer and biochar in paddy soil contaminated by Cd and Pb[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2015, 32(1): 14-19. |
| [10] |
徐升, 弓晓峰. 苎麻修复重金属污染土壤及强化措施研究进展[J]. 广东农业科学, 2014, 41(17): 153-159, 169. XU Sheng, GONG Xiao-feng. Research progress in ramie remediation and strengthening measures for soil contaminated by heavy metals[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 41(17): 153-159, 169. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2014.17.033 |
| [11] |
郭晓方, 卫泽斌, 丘锦荣, 等. 玉米对重金属累积与转运的品种间差异[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2010, 26(4): 367-371. GUO Xiao-fang, WEI Ze-bin, QIU Jin-rong, et al. Differences between corn cultivars in accumulation and translocation of heavy metals[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2010, 26(4): 367-371. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4831.2010.04.015 |
| [12] |
谭玲.菜心Cd低累积品种对Cd、Pb、Cr多种重金属的吸收特性[D].广州: 暨南大学, 2014. TAN Ling. Absorption characteristics of Cd, Pb, Cr heavy metals in Cd low-accumulation varieties[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University, 2014. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=D526273 |
| [13] |
智杨.大豆品种间镉铅低积累性与品质差异性的评估与相关性[D].沈阳: 东北大学, 2015. ZHI Yang. Evaluation and correlation of low accumulation and quality differences of cadmium and lead in soybean varieties[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2015. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10145-1016011464.htm |
| [14] |
黄志亮.镉低积累蔬菜品种筛选及其镉积累与生理生化特性研究[D].武汉: 华中农业大学, 2012. HUANG Zhi-liang. Screening of cadmium low accumulation vegetable varieties and their cadmium accumulation and physiological and biochemical characteristics[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10504-1012458368.htm |
| [15] |
刘维涛, 周启星, 孙约兵, 等. 大白菜对铅积累与转运的品种差异研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2009, 29(1): 63-67. LIU Wei-tao, ZHOU Qi-xing, SUN Yue-bing, et al. Variety difference of lead accumulation and translocation in Chinese cabbage[J]. China Environmental Science, 2009, 29(1): 63-67. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2009.01.013 |
| [16] |
毛海立, 余荣龙. 铅锌矿渣堆周围农田土壤中铜和铅的分布分析[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2007, 35(25): 7884-7885, 8010. MAO Hai-li, YU Rong-long. Distribution of copper and lead in soil around lead-zinc tailing[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2007, 35(25): 7884-7885, 8010. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2007.25.080 |
| [17] |
娄伟.镉铅低累积萝卜、胡萝卜、茄子品种筛选及萝卜镉累积规律研究[D].武汉: 华中农业大学, 2010. LOU Wei. Screening of cadmium and lead low accumulation radish, carrot and eggplant varieties and accumulation of cadmium in radish [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10504-1010010373.htm |
| [18] |
Cid C V, Rodriguez J H, Salazar M J, et al. Effects of co-cropping Bidens pilosa(L.) and Tagetes minuta(L.)on bioaccumulation of Pb in Lactuca sativa(L.)growing in polluted agricultural soils[J]. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 2016, 18(9): 908-917. DOI:10.1080/15226514.2016.1156636 |
| [19] |
Jiang C, Wu Q T, Sterckeman T, et al. Co-planting can phytoextract similar amounts of cadmium and zinc to mono-cropping from contaminated soils[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2010, 36(4): 391-395. DOI:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2009.11.005 |
| [20] |
黑亮, 吴启堂, 龙新宪, 等. 东南景天和玉米套种对Zn污染污泥的处理效应[J]. 环境科学, 2007, 28(4): 852-858. HEI Liang, WU Qi-tang, LONG Xin-xian, et al. Effect of co-planting of Sedum alfredii and Zea mays on Zn-contaminated sewage sludge[J]. Environmental Science, 2007, 28(4): 852-858. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2007.04.028 |
| [21] |
蒋成爱, 吴启堂, 吴顺辉, 等. 东南景天与不同植物混作对土壤重金属吸收的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2009, 29(9): 985-990. JIANG Cheng-ai, WU Qi-tang, WU Shun-hui, et al. Effect of cocropping Sedum alfredii with different plants on metal uptake[J]. China Environmental Science, 2009, 29(9): 985-990. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2009.09.017 |
| [22] |
冯子龙, 卢信, 张娜, 等. 农艺强化措施用于植物修复重金属污染土壤的研究进展[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2017, 45(2): 14-20. FENG Zi-long, LU Xin, ZHANG Na, et al. Advances in research on agronomic intensification measures for phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(2): 14-20. |
| [23] |
于祎飞, 李保国, 齐国辉, 等. 土壤农艺调控措施对苹果和果园土壤镉污染的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2010, 24(2): 197-200, 204. YU Yi-fei, LI Bao-guo, QI Guo-hui, et al. Effects of several agronomy regulations on soil cadmium pollution in the apple orchard[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2010, 24(2): 197-200, 204. |
| [24] |
窦春英.施肥对东南景天吸收积累锌和镉的影响[D].杭州: 浙江林学院, 2009. DOU Chun-ying. Effect of fertilization application on soil heavy metal phytoremediation by Sedum alfredii[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang A & F University, 2009. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10341-2009199518.htm |
| [25] |
李贺.不同农艺措施对黑麦草、地肤、遏蓝菜修复Cd污染土壤的影响[D].乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2013. LI He. The effects of Perennial ryegrass, Kochia scoparia, Thlaspi arvense on Cd contaminated soil with different agronomic measures[D]. Urumchi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2013. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=D368843 |
| [26] |
李廷强, 杨肖娥, 龙新宪. 东南景天提取污染土壤中锌的潜力研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 2004, 18(6): 79-83. LI Ting-qiang, YANG Xiao-e, LONG Xin-xian. Zinc phytoextraction ability from polluted soil of hyperaccumulating ecotype of Sedum alfredii Hance[J]. Journal of Soil Water Conservation, 2004, 18(6): 79-83. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2004.06.019 |
| [27] |
汤海涛, 李卫东, 孙玉桃, 等. 不同叶面肥对轻度重金属污染稻田水稻重金属积累调控效果研究[J]. 湖南农业科学, 2013(1): 40-44. TANG Hai-tang, LI Wei-dong, SUN Yu-tao, et al. Controlling effects of different foliar fertilizers on heavy metal accumulation in rice plant in mild heavy metal polluted paddy field[J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2013(1): 40-44. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-060X.2013.01.012 |
| [28] |
苟文龙, 李元华, 万勤明, 等. 尿素不同施用量对多花黑麦草产草量及经济效益的影响[J]. 草业与畜牧, 2015(6): 20-21, 59. GOU Wen-long, LI yuan-hua, WAN Qin-ming, et al. Effects of additional urea application levels on grass yield and economic benefits of italian ryegrass[J]. Prataculture & Animal Husbandry, 2015(6): 20-21, 59. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-8403.2015.06.005 |
| [29] |
廖晓勇, 陈同斌, 谢华, 等. 磷肥对砷污染土壤的植物修复效率的影响:田间实例研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2004, 24(3): 455-462. LIAO Xiao-yong, CHEN Tong-bin, XIE Hua, et al. Effect of application of P fertilizer on efficiency of As removal from As contaminated soil using phytoremediation: Field study[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2004, 24(3): 455-462. |
| [30] |
丁凌云, 蓝崇钰, 林建平, 等. 不同改良剂对重金属污染农田水稻产量和重金属吸收的影响[J]. 生态环境, 2006, 15(6): 1204-1208. DING Ling-yun, LAN Chong-yu, LIN Jian-ping, et al. Effects of different amendments on rice yield and heavy metal absorption in heavy metal contaminated farmland[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2006, 15(6): 1204-1208. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2006.06.016 |
| [31] |
于祎飞.土壤镉污染及农艺调控对苹果树体镉积累影响的研究[D].保定: 河北农业大学, 2011. YU Wei-fei. Effects of soil cadmium pollution and agronomic regulation on cadmium accumulation in apple trees[D]. Baoding: Agricultural University of Hebei, 2011. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11920-1011074610.htm |
| [32] |
王世华, 罗群胜, 刘传平, 等. 叶面施硅对水稻籽实重金属积累的抑制效应[J]. 生态环境, 2007, 16(3): 875-878. WANG Shi-hua, LUO Qun-sheng, LIU Chuan-ping, et al. Inhibitory effect of foliar application of silicon on accumulation of heavy metals in rice seeds[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2007, 16(3): 875-878. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2007.03.034 |
| [33] |
刘霞, 王建涛, 张萌, 等. 螯合剂和生物表面活性剂对Cu、Pb污染塿土的淋洗修复[J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(4): 1590-1597. LIU Xia, WANG Jian-tao, ZHANG Meng, et al. Remediation of CuPb-contaminated loess soil by leaching with chelating agent and biosurfactant[J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(4): 1590-1597. |
| [34] |
Yang R, Luo C, Zhang G, et al. Extraction of heavy metals from ewaste contaminated soils using EDDS[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2012, 24(11): 1985-1994. DOI:10.1016/S1001-0742(11)61036-X |
| [35] |
赵娜, 崔岩山, 付彧, 等. 乙二胺四乙酸(EDTA)和乙二胺二琥珀酸(EDDS)对污染土壤中Cd、Pb的浸提效果及其风险评估[J]. 环境化学, 2011, 30(5): 958-963. ZHAO Na, CUI Yan-shan, FU Yu, et al. Extraction of Cd and Pb from contaminated soil by ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid(EDTA) and ethylenediamine disuccinic acid (EDDS) and its risk assessment[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2011, 30(5): 958-963. |
| [36] |
Zhang H, Gao Y, Xiong H. Removal of heavy metals from polluted soil using the citric acid fermentation broth: a promising washing agent[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(10): 9506-9514. DOI:10.1007/s11356-017-8660-y |
| [37] |
Wang J, Jiang J, Li D, et al. Removal of Pb and Zn from contaminated soil by different washing methods: The influence of reagents and ultrasound[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(24): 20084-20091. DOI:10.1007/s11356-015-5219-7 |
| [38] |
平安, 南绘. 有机酸对土壤重金属的浸提效果研究[J]. 农业科技与装备, 2011(6): 24-25, 28. PING An, NAN Hui. Effect of organic acids on the extraction of heavy metals[J]. Agricultural Science & Technology and Equipment, 2011(6): 24-25, 28. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-1161.2011.06.010 |
| [39] |
许中坚, 许丹丹, 郭素华, 等. 柠檬酸与皂素对重金属污染土壤的联合淋洗作用[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(8): 1519-1525. XU Zhong-jian, XU Dan-dan, GUO Su-hua, et al. Combined leaching of heavy metals in soil by citric acid and saponin[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2014, 33(8): 1519-1525. |
| [40] |
许端平, 李晓波. 有机螯合剂对污染土壤中Pb和Cd淋洗修复研究[J]. 地球环境学报, 2015, 6(2): 120-126. XU Duan-ping, LI Xiao-bo. Removing Pb and Cd from soil by organic chelators[J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2015, 6(2): 120-126. |
| [41] |
魏世强, 木志坚, 青长乐. 几种有机物对紫色土镉的溶出效应与吸附-解吸行为影响的研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2003, 40(1): 110-117. WEI Shi-qiang, MU Zhi-jian, QING Chang-le. Effects of several organic substances on the solubility and adsorption-desorption behaviors of cadmium in purplish soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2003, 40(1): 110-117. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2003.01.015 |
| [42] |
Maity J P, Huang Y M, Hsu C M, et al. Removal of Cu, Pb and Zn by foam fractionation and a soil washing process from contaminated industrial soils using soapberry-derived saponin: A comparative effectiveness assessment[J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 92(10): 1286-1293. DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.04.060 |
| [43] |
常红, 李利芬, 黄丽. 皂角苷对红壤和黄褐土中Pb2+、Zn2+的解吸特征[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(1): 93-100. CHANG Hong, LI Li-fen, HUANG Li. Desorption characteristics of Pb2+ and Zn2+ from red soil and yellow-cinnamon soil by saponin[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2017, 36(1): 93-100. |
| [44] |
张中文.茶皂素对土壤重金属污染淋洗修复的影响研究[D].泰安: 山东农业大学, 2009. ZHANG Zhong-wen. Study on the effect of tea saponin on the leaching and repair of heavy metal pollution in soil[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2009. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10434-2009234537.htm |
| [45] |
Han D H, Lee J H. Effects of liming on uptake of lead and cadmium by Raphanus sativa[J]. Archives of environmental contamination and Toxicology, 1996, 31(4): 488-493. |
| [46] |
Ruttens A, Colpaert J V, Mench M, et al. Phytostabilization of a metal contaminated sandy soil. Ⅱ: Influence of compost and /or inorganic metal immobilizing soil amendments on metal leaching[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2006, 144(2): 533-539. |
| [47] |
Yang J, Mosby D. Field assessment of treatment efficacy by three methods of phosphoric acid application in lead-contaminated urban soil[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2006, 366(1): 136-142. |
| [48] |
Zhu J, Cai Z, Su X, et al. Immobilization and phytotoxicity of Pb in contaminated soil amended with γ-polyglutamic acid, phosphate rock, and γ-polyglutamic acid-activated phosphate rock[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 2(4): 2661-2667. |
| [49] |
Yao A, Wang Y, Ling X, et al. Effects of an iron-silicon material, a synthetic zeolite and an alkaline clay on vegetable uptake of As and Cd from a polluted agricultural soil and proposed remediation mechanisms[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2017, 39(2): 353-367. DOI:10.1007/s10653-016-9863-8 |
| [50] |
张燕, 铁柏清, 刘孝利, 等. 玉米秸秆生物炭对稻田土壤砷、镉形态的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(2): 715-721. ZHANG Yan, TIE Bo-qing, LIU Xiao-li, et al. Effects of waterlogging and application of bio-carbon from corn stalks on the physico-chemical properties and the forms of arsenic and cadmium in arsenic and cadmium-contaminated soils[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(2): 715-721. |
| [51] |
石红蕾, 周启星. 生物炭对污染物的土壤环境行为影响研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 2014, 33(2): 486-494. SHI Hong-lei, ZHOU Qi-xing. Research progresses in the effect of biochar on soil-environmental behaviors of pollutants[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2014, 33(2): 486-494. |
| [52] |
郭文娟, 梁学峰, 林大松, 等. 土壤重金属钝化修复剂生物炭对镉的吸附特性研究[J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(9): 3716-3721. GUO Wen-juan, LIANG Xue-feng, LIN Da-song, et al. Adsorption of Cd2+ on biochar from aqueous solution[J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(9): 3716-3721. |
| [53] |
Qiu Z, Chen J, Tang J, et al. A study of cadmium remediation and mechanisms: Improvements in the stability of walnut shell-derived biochar[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 636: 80-84. DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.215 |
| [54] |
Jung K W, Lee S Y, Lee Y J. Facile one-pot hydrothermal synthesis of cubic spinel-type manganese ferrite /biochar composites for environmental remediation of heavy metals from aqueous solutions[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 261: 1-9. DOI:10.1016/j.biortech.2018.04.003 |
| [55] |
杜志敏, 郝建设, 周静, 等. 四种改良剂对铜和镉复合污染土壤的田间原位修复研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2012, 49(3): 508-517. DU Zhi-min, HAO Jian-she, ZHOU Jing, et al. Field in-situ remediation of Cu-Cd polluted soil by four amendments[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2012, 49(3): 508-517. |
| [56] |
陈展祥, 陈传胜, 陈卫平, 等. 凹凸棒石及其改性材料对土壤镉生物有效性的影响与机制[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(10): 4744-4751. CHEN Zhan-xiang, CHEN Chuan-sheng, CHEN Wei-ping, et al. Effect and mechanism of attapulgite and its modified materials on bioavailability of cadmium in soil[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(10): 4744-4751. |
| [57] |
Mao X, Wang L, Gu S, et al. Synthesis of a three-dimensional network sodium alginate-poly(acrylic acid) /attapulgite hydrogel with good mechanic property and reusability for efficient adsorption of Cu2+ and Pb2+[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2018, 16(2): 653-658. |
| [58] |
邓腾灏博, 谷海红, 仇荣亮. 钢渣施用对多金属复合污染土壤的改良效果及水稻吸收重金属的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2011, 30(3): 455-460. DENG Teng-hao-bo, GU Hai-hong, QIU Rong-liang. Ameliorative effects of steel slag application on multi-metal contaminated soil and heavy metal uptake of rice[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2011, 30(3): 455-460. |
| [59] |
陈晓, 侯文华, 汪群慧. 电炉钢渣对水中Cu2+、Cd2+和Pb2+的去除作用[J]. 环境科学, 2009, 30(10): 2940-2945. CHEN Xiao, HOU Wen-hua, WANG Qun-hui. Removal of metal ions Cu2+, Cd2+and Pb2+ from solutions by sorption on slag[J]. Environmental Science, 2009, 30(10): 2940-2945. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2009.10.021 |
| [60] |
董黎静, 朱志良, 仇雁翎, 等. 羟基磷灰石及其复合材料对重金属的吸附研究进展[J]. 化学通报, 2013, 76(5): 405-410. DONG Li-jing, ZHU Zhi-liang, QIU Yan-ling, et al. Advance in research of heavy metals removal by hydroxyapatite and its composite[J]. Chemistry, 2013, 76(5): 405-410. |
| [61] |
邢金峰, 仓龙, 葛礼强, 等. 纳米羟基磷灰石钝化修复重金属污染土壤的稳定性研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2016, 35(7): 1271-1277. XING Jin-feng, CANG Long, GE Li-qiang, et al. Long-term stability of immobilizing remediation of a heavy metal contaminated soil with nano-hydroxyapatite[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2016, 35(7): 1271-1277. |
| [62] |
Zhang Z, Li M, Chen W, et al. Immobilization of lead and cadmium from aqueous solution and contaminated sediment using nano-hydroxyapatite[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2010, 158(2): 514-519. |
| [63] |
Mavropoulos E, Rossi A M, Costa A M, et al. Studies on the mechanisms of lead immobilization by hydroxyapatite[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2002, 36(7): 1625-1629. |
| [64] |
Hartley W, Lepp N W. Remediation of arsenic contaminated soils by iron-oxide application, evaluated in terms of plant productivity, arsenic and phytotoxic metal uptake[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2008, 390(1): 35-44. |
| [65] |
杨俊兴, 陈世宝, 郭庆军. 赤泥在重金属污染治理中的应用研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 2013, 32(7): 1937-1944. YANG Jun-xing, CHEN Shi-bao, GUO Qing-jun. Application of red mud in the remediation of heavy metals pollution: A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2013, 32(7): 1937-1944. |
| [66] |
黄蔼霞, 许超, 吴启堂, 等. 赤泥对重金属污染红壤修复效果及其评价[J]. 水土保持学报, 2012, 26(1): 267-272. HUANG Ai-xia, XU Chao, WU Qi-tang, et al. Remediation effects and their evaluation of red mud amendment in heavy metal polluted red soil[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2012, 26(1): 267-272. |
| [67] |
Gray C W, Dunham S J, Dennis P G, et al. Field evaluation of in situ remediation of a heavy metal contaminated soil using lime and redmud[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2006, 142(3): 530-539. |
| [68] |
李韵诗, 冯冲凌, 吴晓芙, 等. 重金属污染土壤植物修复中的微生物功能研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(20): 6881-6890. LI Yun-shi, FENG Chong-ling, WU Xiao-fu, et al. A review on the functions of microorganisms in the phytoremediation of heavy metalcontaminated soils[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(20): 6881-6890. |
 2019, Vol. 38
2019, Vol. 38