文章信息
- 詹 杰, 魏树和, 牛荣成
- ZHAN Jie, WEI Shu-he, NIU Rong-cheng
- 我国稻田土壤镉污染现状及安全生产新措施
- Advances of Cadmium Contaminated Paddy Soil Research and New Measure of Its Safe Production in China: A Review
- 农业环境科学学报, 2012, 31(7): 1257-1263
- Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2012, 31(7): 1257-1263
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2011-11-04
2.辽宁职业卫生技术学院, 沈阳 110101;
3 中国科学院研究生院, 北京 100039
2.College of Liaoning Professional Sanitation Technology, Shenyang 110101, China;
3.Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100039, China
我国是世界上最大的水稻生产和消费国,水稻也 是我国的第一大粮食作物,年种植面积约2 860 万 hm2 ,占全球水稻种植面积的 1/5; 我国常年水稻产量 约占粮食总产量的 40%,年产稻米 1.85 亿 t,占世界 总产量的 1/3。 因此,水稻生产在保障我国粮食安全中 担当第一重任,对确保世界粮食安全也具有举足轻重 的作用 [1] 。然而,随着我国工业化进程的加速和社会经 济的发展,重金属污染问题日趋严峻,水稻的生产受 重金属镉污染的影响也日益加剧,严重威胁着粮食生 产安全 [2,3] 。 因此,如何控制水稻镉污染并实现其安全 生产 ( 主要是卫生品质安全 ) 值得关注。 本文对我国稻田土壤及稻米镉污染现状进行了综述,对现有的镉 污染稻田改良及钝化修复方法进行了归纳总结并指 出其存在的弱点,在此基础上,试图从排型水稻 品种方面提出镉污染农田安全利用的新方法。 1 我国稻田土壤及稻米 Cd 污染现状
在我国,关于水稻生产受镉污染状况的大面积 普查研究还未见报道,不同的学者根据不同地区的 稻田土壤及稻米镉污染情况进行了相关研究。1989 年就有报道表明,我国 11 个灌区遭受镉 ( Cd ) 污染农 田面积达 12 000 hm2 。 沈阳张士灌区一闸严重污染区 土壤 Cd 含量高达 5~7 mg · kg-1 ,稻米 Cd 含量也达 1~ 2 mg · kg-1 ,严重超过了我国无公害稻米中重金属含 量标准 ( NY 5115—2008 ) [4] 。土壤污染主要是因含工 业污水灌溉造成的,Cd 主要分布在土壤表层,这些污 染土壤虽早已停止污灌,但 Cd 污染仍然存在,且有 向下游散的趋势。王凯荣总结了中国 16 个工矿污 染区农田土壤和稻米中 Cd 含量的状况,发现这些地 方受 Cd 污染的程度已相当严重 [5] 。其污染主要是因 金属采矿废弃物堆放及矿山废水造成的,主要分布在 矿区周围。 之后,重金属尤其是Cd 污染稻米事件常有 报道,污染土壤的途径也主要是污灌或金属采矿及 冶炼造成的。 如浙江省遂昌县和温州地区曾相继出现 Cd 中毒事件,上述两地的糙米 Cd 含量分别达到 1.17 mg · kg-1 和 1.30 mg · kg-1[6] 。 福建省各主要稻区 Cd 的稻 米重金属污染不容乐观,特别是 Cd 含量几乎均超标 [7] 。 刘洪莲等对太湖地区几种类型水稻土进行研究,结果 表明 Cd 的积累速率达到 0.3~3 滋g · kg-1 · a-1 ,年污染通 量为 0.8伊10-3~10伊10-3kg · hm-2· a-1 ,整个区域 Cd 的污 染通量较国际上的报道偏高,说明该地区土壤环境污 染较为严重 [8] 。 Yang 等抽样调查了广东省乐昌铅锌矿 周边采矿废水灌溉 0.8 hm2 稻田土壤及稻米中 Cd 的 污染情况,结果表明,稻田土壤中 Cd 含量最大值为 29.68 mg · kg-1 ,最小值为 2.01 mg · kg-1 ,平均为 13.59 mg · kg-1 ,稻米中 Cd 含量平均为 0.24 mg · kg-1[9] 。王昌 全等研究表明,成都平原 (广汉、 德阳、 新都等) 13 个 市 ( 县、 区 ) 在主要耕种制度为稻-麦轮作制条件下,稻 米中 Cd 含量超标达 8.70% [10] 。Zhai 等采样测定了湖 南省矿业城市郴州 2 415 km2 稻田土壤及稻米中 Cd 的含量,土壤 Cd 含量为 2.72~4.83 mg · kg-1 ,几何平 均值为 1.45 mg · kg-1 ; 相应的,稻米中 Cd 含量为 0.01~ 4.43 mg · kg-1 ,平均值为 0.39 mg · kg-1 ,超标严重 [11] 。 甄 燕红等随机抽取国内部分市场的精米样品 ( 44 个籼 米和 47 个粳米样品),对样品中 Cd 含量的测定结果 表明,91 个样品中 Cd 含量超标达 10%左右 [12] 。由于 是市场随机取样的结果,对于稻米的准确来源无法确 定,也就无法确定其污染源,但也说明一定量的 Cd 污染稻米是确实存在的。 Sun 等研究了湖南省凤凰县 茶田镇汞矿周围 18 个稻田土壤及相应的水稻样品中 Cd 含量,结果表明,有 4 个土壤样 品中 Cd 含 量 超 标,Cd 含量为 0. 53 ~14. 91 mg · kg-1 ,几何平均值为 1.05 mg · kg-1 。相应的,稻米中 Cd 含量为 0.25~0.54 mg · kg-1 ,严重超标 [13] 。Zhao 等按照1颐50 000 比例土地 使用图,采样测定了浙江省温岭地区 96 个稻田土壤 及相应的水稻样品中 Cd 含量,结果表明,有 4 个土 壤样品中 Cd 含量超标,Cd 含量为 0.11~0.45 mg · kg-1 , 平均值为 0.31 mg · kg-1 ;相应的,稻米中 Cd 含量为 0.002 ~0.467 mg · kg-1 ,平均值为 0.072 mg · kg-1 ,部分 样品超标 [14] 。肖俊清等研究表明,长江三角州地区水 稻普遍遭遇了重金属元素污染,果实中 Cd、 Cr、 Cu、 Hg 和 Zn 含 量 分 别 是 背景 值 的 3.1、 2.7、 1.5、 1.1 和 1.1 倍,有 29.5%、 5.8%、 1.4%样品中的 As、 Cd 和 Pb 含量 超标。这一地区工矿企业密集,污染土壤多是因工业 废水的不合理排放造成的 [15] 。
上述这些研究虽然地域分散,在全国范围内不 具有系统性、 全面性,但也基本呈现出一些特点: 即污 染区域多分布在污灌区、 金属采矿区、工业区和乡镇 企业周围,在南方经济相对发达地区具有一定的普遍 性,这些地区的污染土壤至今没有得到有效的控制与 修复,且有污染面积继续扩大的趋势。 更为严重的是, 这些污染土壤绝大多数仍然在从事农业生产活动,虽 然部分污染土壤转变了耕作方式,但仍然存在着一定 的环境风险。 因此,上述研究也在一定程度上表明,我 国水稻生产确实存在 Cd 污染风险,在某些地区还相 当严重。 有必要采用一些措施改善这种状况以确保稻 米的安全生产。 2 Cd 污染稻田土壤改良剂研究
对于大面积污染农田来说,人们试图采取一些 钝化方法,降低污染土壤中重金属的生物有效性,进 而阻止其对农作物的污染,使一些污染程度较低的农 田还可以继续安全的生产农产品。 这一方法的主要原 理就是通过向污染土壤中施加一些物质,以改变重 金属在土壤中的存在状态,降低其在土壤中的迁移性 和生物可利用性,使土壤中重金属钝化,进而减少作 物对重金属的富集,从而减少重金属对作物的危害及潜在的健康风险,施加的物质常常叫做钝化剂。然 而,土壤钝化剂的施入会不同程度地改变土壤的物 理、化学性质。较好的作用是在不造成土壤二次污染 的同时,也能对污染土壤的一些理化性质进行改良, 这类施加物质统称为土壤改良剂更具实践意义。
关于我国稻田 Cd 污染土壤改良剂及其改良效 果的研究已有很多,根据改良剂的来源,大体可将改 良剂分为无机型、有机型以及无机与有机混合型 3 大 类。无机型改良剂方面,最常见的是一些工业用料或 废料,如石灰 [16,17,20] 、 海泡石 [16] 、 Na2SO4[19] ,以及一些天 然物质如高岭土 [16] 。屠乃美等利用小区试验,研究了 投加低中高 3 种不同剂量的石灰、 钙镁磷肥、 海泡石 或高岭土对晚稻 V647 富集 Cd 的影响。 结果表明,石 灰和钙镁磷肥的作用主要是土壤 pH 值和降低土壤 中 Cd 的有效性,海泡石和高岭土的改良机制主要在 于通过对 Cd 的吸附作用而降低其有效性。综合来 看,以钙镁磷肥中量处理和海泡石中量处理效果为最 佳 [16] 。 宗良纲等利用土壤盆栽试验方法,设置高低 2 种施加剂量,认为硅肥的改良效果最好,其次是钙镁 磷肥,然后是石灰 [17] 。 丁凌云等探讨了石灰、过磷酸钙 和有机物料及其不同组合对盆栽污染土壤中水稻 Cd 富集的影响,认为石灰+过磷酸钙对于降低水稻体内 的重金属含量效果最好 [18] 。 Li 等利用盆栽试验比较了 7 种施加物料 (石灰、 猪粪、 泥碳、 紫云英、 硅酸钙、 钙 镁磷肥、 ZnSO 4 ) 对水稻富集 Cd 的影响,其中以石灰 的效果最好 [19] 。上述 4 个试验中,石灰的使用最为 广泛,修复效果也较好,这与其所具有的碱性条件有 关。但不同学者之间的结果也有一定差异,这可能是 施加量大小、 土壤质地等因素造成的。此外,施加不同 剂量的 Na2SO4、 CaO、 CaCO3、 CaSO 4、 赤泥也可以通过 降低土壤中 Cd 的有效态含量以降低稻米中 Cd 含 量 [20,21,22] 。肥料的施用也具有明显的改良作用,其中磷 肥和氮肥研究的较多,如钙镁磷肥 [16 ,20,23] 以及氨态氮、 硝态氮、 尿素 [24,25,26] 。 对于硅肥的改良效果也取得了一 定进展 [16] 。 有机型改良剂方面,研究较多是将一些有 机物料粉碎后施入 Cd 污染土壤,以降低土壤中 Cd 的生物有效性,如苜蓿、 稻草粉 [27] 、 稻草、 紫云英 [28] 、 植 物叶 [29] 、 油菜籽壳 [30] ,以及混合有机肥料或猪厩肥 [30,31] 。 此外,在有机酸和 EDTA 的改良作用方面也进行了一 些研究 [32] 。而复合型改良剂则主要是上述无机与有机 改良剂的简单配制,如石灰与过磷酸钙及有机物料的 混合物 [33] 。在人为精细加工复配改良剂方面涉及得很 少 [34] 。与上述研究结果相类似,这些物料的施用一方 面提高了水稻的产量,另一方也通过降低土壤中 Cd 的有效性以降低稻米对 Cd 的富集,改良机理基本是 一致的,即主要通过吸附及螯合钝化作用或提高土 壤 pH 值等达到钝化土壤中的 Cd 的目的,这里不一 一赘述。
总的来看,在改良土壤环境方面,有机物料的效 果较为突出。在土壤中 Cd 的有效性降低方面,无机 物料更强一些。 因此,有机与无机物料的混合使用成 为当前研究的重要方向。 我国虽在改良剂改良效果比 较研究中取得较大进展,但在改良剂粒径对污染土壤 改良效果方面涉及较少,在改良剂产业化方面进展也 很缓慢,这主要是因为单纯地依靠改良剂的作用还 无法达到污染土壤安全生产的要求,还需要寻找新的 安全生产途径。 3 利用排异型水稻品种的安全生产思路
土壤改良剂法虽然具有操作简单、 可以大面积实 施以及短时间内见效快等优点,但污染土壤中的重金 属毕竟还留在土壤中,一旦环境条件发生变化,被钝 化了的重金属还有可能被释放出来,仍然具有潜在的 环境风险。
一般来说,在得知土壤受到重金属污染后,是不 能用于粮食生产的,这一点在西方发达国家执行得尤 为彻底。在我国,重金属污染农田上农作物安全生产 问题最初主要来自于人们在未知农田受到污染的条 件下产生的。 这主要是因为一方面当地人们确实不知 道所种植的农田已遭到了重金属污染;另一方面,科 研部门虽测知该地块受到了污染,却无法与当地农 民沟通使之明了实情。 这些情况就使得我国污染农田 仍然在照常进行农业生产活动,所生产的粮食也就自 然存在质量安全隐患。基于我国的国情,受污染农田 若都不用来农业生产而改为它用也不现实。 若等到污 染土壤修复好后再使用,现有的修复技术在短时间内 也很难实现。为此,在一定条件下种植一些排型作 物品种就成为一种较新颖也比较实际的安全生产措 施。因为这种措施就算在没有污染的地块上,农产品 也可以照样正常生产,适用性比传统的农业生产更为 广泛。
那么,什么是排型作物品种呢? 魏树和和周启 星等认为排型作物是指能在重金属污染土壤上正 常生长,植物有利用价值部位重金属的含量均较低, 但是一旦土壤污染物含量超过了一定阈值,该作物的 排异机理将无法继续限制污染物向有利用价值的部位转移 [35] 。 与此相类似的提法还有低积累作物品种以 及污染安全品种等 [36,37,38] ,其核心内容还是要求对重金 属积累的含量较低,至少要低于我国无公害稻米中重 金属含量标准 ( NY 5115—2008 )。
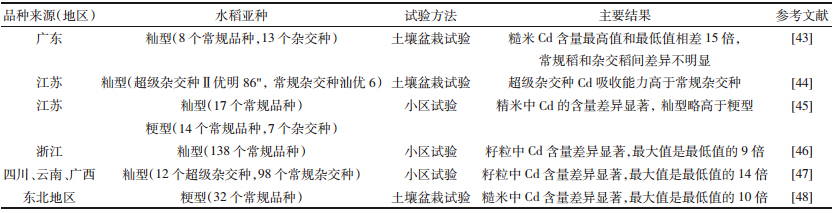
我国水稻品种资源丰富,南方主要以籼型为主, 北方主要以粳型为主。籼稻中,常规稻、 三系杂交稻、 二系杂交稻以及超级稻均有较大的种植面积,而粳型 水稻主要以常规稻为主。 不同学者主要采用小区试验 和盆栽试验的方式,对不同水稻品种富集 Cd 的情况 进行了研究,并发现不同品种稻米对 Cd 的富集存在 着显著差异。 李正文等采用小区试验的方法,对江苏、 浙江和上海地区常用中粳稻的 57 个品种稻米 Cd 富 集情况进行了研究,结果表明,稻米中 Cd 含量范围 为 0.026~0.099 mg · kg-1 ,变异系数达 39.4%,品种间差 异显著 [39] 。仲维功等采用小区试验的方法,比较了主 要来自江苏省、 湖南省、 云南省、 广东省和江西省,美 国、 国际水稻研究所、 印度和日本的 7 份杂交稻品种, 16 份常规籼稻品种,20 份常规粳稻品种精米中 Cd 含量的差情况,除显示品种间有显著差异外,还呈 现常规籼稻精米含量最高,杂交稻精米含量居中,常 规稻精米含量最低的趋势 [36] 。 曾翔等采用土壤盆栽试 验方法,以 7 个类型 46 个水稻品种为试材,发现在 土壤含 Cd 量为 2 mg · kg-1 时,46 种水稻糙米含 Cd 量 变化范围为 0.428~2.558 mg · kg-1 。7 种类型水稻糙米 含 Cd 量从高到低依次为特种稻、 常规早籼稻、 三系 杂交晚稻、 两系杂交晚稻、 常规晚籼稻、 常规粳稻、 爪 洼稻 [40] 。在浙江省晚粳稻主产区嘉兴、 湖州、 杭州、 宁 波、 绍兴市的 6 个大田试点的 12 个晚粳稻糙米及精 米中 Cd 的含量也具有显著差异 [41] 。Yu等采用土壤 盆栽试验以籼型稻的 20 个常规品种和 23 个杂交种 为试材,发现糙米 Cd 含量最高值和最低值相差近 6 倍,杂交稻 Cd 含量略高于常规稻 [42] 。其他的学者也 有类似的发现,如表 1 所示。上述研究表明,不同品种 稻米对 Cd 的富集呈现出显著的差异性,并略呈现出 杂交稻富集程度高于常规稻,籼稻高于粳稻的趋势。 但这种趋势因供试品种不同而有很大差异。总体上来 看,确有一些水稻品种对 Cd 具有低积累性或者说是 排异性,这为 Cd 污染土壤安全生产提供了新的研究 思路,也正成为未来农业环境领域研究的一个新的方 向和热点。
上述研究表明 (表 1 ) ,从现有水稻品种筛选排异 型品是切实可行的,而且发现了一些具有排异型特 征品种。事实上,这种品种间的差异也可能与品种间 基因差异有关。如 Clarke 等认为,硬粒小麦低 Cd 积 累的性状是由单基因控制的且具有较强的遗传稳定 性[49,50] 。这一发现在低积累品种育种研究方面具有十 分重要的意义,或许为低积累品种选育提供一条新的 途径。
 |
确保 Cd 污染稻田水稻安全生产的最好办法当 然是将污染了的稻田加以修复,修复 Cd 污染稻田土 壤最理想的方式就是将 Cd 从土壤中去除,这些方法 如淋洗和植物提取修复等。然而,淋洗方法对于大面 积的污染农田来说,还很难应用。 利用超富集植物的 超量提取作用去除污染土壤中重金属的技术虽表现 出较好前景,但因其修复时间长、 修复效率有限、 修复 植物生物量难以处理等问题,也无法大面积应用。况 且,将大面积污染土壤长期闲置不用或用于植物修复 也很难创造出可观的经济效益,对于我国人多地少的 国情也不适宜。因此,在土壤中 Cd 的去除修复技术 无法在短时间内实现的前提下,Cd 排异型水稻品种 的筛选与利用是实现其安全生产的一个新的有效措 施。 排异型作物虽可以在一定污染水平条件下的农田 上正常生长并生产了符合标准的农产品,但由于污 染土壤的不均一性,在局部仍然存在因重金属含量过高而导致农产品中重金属含量过高的风险。 如果在 使用排异型作物生产之前,施加污染土壤改良剂,不 但会降低这种风险,也会进一步提高排异型作物的适 用范围。 因此,土壤改良剂与排异型作物的联合使用 应是一种较好的选择。
| [1] | 唐绍清. 稻米蒸煮和营养品质性状的QTL定位[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2007. Tang Shao-qing. Mapping of QTL for cooking and nutrient quality traits of rice[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2007. |
| [2] | 赵 雄, 李福燕, 张冬明, 等. 水稻土镉污染与水稻镉含量相关性研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2009, 28(11) : 2236-2240. Zhao Xiong, Li Fu-yan, Zhang Dong-min, et al. Relationship between paddy soils cadmium pollution and cadmium content in Rice[J]. J ournal of Agro-Environment Sc ience, 2009, 28(11) : 2236-2240. |
| [3] | 肖相芬, 张经廷, 周丽丽, 等. 中国水稻重金属镉与铅污染 GAP 栽培控制关键点分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2009, 25(21) : 130-136. Xiao Xiang-fen, Zhang Jing-ting, Zhou Li-li, et al. Analysis on key points for controlling cadmium and lead contamination during rice production[J]. Chines e Agricultural Scie nce Bulletin, 2009, 25(21) : 130-136. |
| [4] | 吴燕玉, 陈 涛, 张学询.沈阳张士灌区镉污染生态的研究[J]. 生态学报, 1989,9(1) : 21-26. Wu Yan-yu, Chen Tao, Zhang Xue-xun. Pollution ecology of Cd in the Zhangshi irrigation area of Shenyang[J]. A CTA Ecologica Sinica, 1989, 9(1) : 21-26. |
| [5] | 王凯荣, 郭 焱, 何电源, 等. 重金属污染对稻米品质的影响的研究[J]. 农业环境保护, 1993,12(6) : 254-257. Wang Kai-rong, Guo yan, He Dian-yuan. Studies on the influences of heavy metal pollution on the qualities of brown rice[J]. Agro-Environmental Protection, 1993,12(6) : 254-257. |
| [6] | 胡培松. 土壤有毒重金属镉毒害及镉低积累型水稻筛选与改良[J]. 中国稻米, 2004, 2: 10-12. Hu Pei-song. Cd toxic in soil and low accumulation rice screening and improving[J]. China Rice , 2004, 2: 10-12. |
| [7] | 肖美秀, 梁义元, 梁康迳, 等. 水稻重金属污染及其控制技术的研究进展[J]. 亚热带农业研究, 2005,1(3) : 40-43. Xiao Mei-xiu, Liang Yi-yuan, Liang Kang-jing, et al. Ad vance in research on pollution of heavy metals in rice and its control technology[J]. Subtropical A griculture Res earch, 2005,1(3) : 40-43. |
| [8] | 刘洪莲, 李艳慧, 李恋卿, 等. 太湖地区某地农田土壤及农产品中重金属污染及风险评价[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2006,6(5) : 60-63. Liu Hong-lian, Li Yan-hui, Li Lian-qing, et al. Pollution and risk evaluation of heavy metals in soil and agro-products from an area in the Taihu Lake region[J]. J ournal of Safety and Environment, 2006,6(5) : 60-63. |
| [9] | Yang Q W, Lan C Y, Wang H B, et al. Cadmium in soilrice system and health risk associated with the use of untreated mining wastewater for irrigation in Lechang, China[J]. Agricultural Wate r Management, 2006, 84: 147-152. |
| [10] | 王昌全, 代天飞, 李 冰, 等. 稻麦轮作下水稻土重金属形态特征及其生物有效性 [J]. 生态学报, 2007, 27(3) : 890-897. Wang Chang-quan, Dai Tian-fei, Li bing, et al. The speciation and bioavailability of heavy metals in paddy soils under the ricewheat cultivation rotation[J]. A cta Ec ologica Sinica , 2007, 27(3) : 890-897. |
| [11] | Zhai L M, Liao X Y, Chen T B, et al. Regional assessment of cadmium pollution in agricultural lands and the potential health risk related to intensive mining activities: A case study in Chenzhou City, China [J]. J ournal of Env ironmental Sciences, 2008,20: 696-703. |
| [12] | 甄燕红, 成颜君, 潘根兴, 等. 中国部分市售大米中Cd、 Zn、 Se 的含 量及其食物安全评价[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2008,8(1) : 119-122. Zhen Yan-hong, Cheng Yan-jun, Pan Gen-xing, et al. Cd, Zn and Se content of the polished rice samples from some Chinese open markets and their relevance to food safety [J]. J ournal of Safety and Environment , 2008,8(1) : 119-122. |
| [13] | Sun H F, Li Y H, Ji Y F, et al. Environmental contamination and health hazard of lead and cadmium around Chatian mercury mining deposit in western Hunan Province, China[J]. Trans Nonferrous Metal Social, China, 2010,20:308-314. |
| [14] | Zhao K L, LiuX M, Xu J M, et al. Heavy metal contaminations ina soil-rice system: Identification of spatial dependence in relation to soil properties of paddy fields [J]. J ournal of Hazardous Materials , 2010, 181:778-787. |
| [15] | 肖俊清, 袁旭音, 李继洲. 长江三角洲地区土壤和水稻重金属污染特征研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2010, 38(19) : 10206-10208. Xiao Jun-qing, Yuan Xu-yin, Li Ji-zhou. Characteristics of heavy metal pollution in soil and rice of Yangtze River delta region[J]. J ournal of A nhui A gricultural Sciences, 2010, 38(19) : 10206-10208. |
| [16] | 屠乃美, 郑 华, 邹 永, 等. 不同改良剂对铅镉污染稻田的改良效应研究[J].农业环境保护, 2000, 19(6): 324-326. Tu Naimei, Zheng Hua, Zou Yong, et al. Effects of different modifier oil rice growth and Pb 驭 Cd contents of rice and soil in Pb-Cd-con taminated paddy field [J]. Agro-Environmental Protection, 2000, 19(6): 324-326. |
| [17] | 宗良纲, 张丽娜, 孙静克, 等.3种改良剂对不同土壤一水稻系统中Cd 行为的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2006,25(4): 834-840. Zong Liang-gang, Zhang Li-na, Sun Jing-ke, et al. Effects of threeamendments on behaviors of cadmium in different soil-rice system [J]. J ournal ofA A gro-Environme nt Science, 2006, 25(4): 834-840. |
| [18] | 丁凌云, 蓝崇钰, 林建平, 等. 不同改良剂对重金属污染农田水稻产量和重金属吸收的影响. 生态环境, 2006, l5(6): 1204-1208. Ding Ling-yun, Lan Chong-yu, Lin Jian-ping, et al. Effects of different ameliorations on rice production and heavy metals uptake by rice grown on soil contaminated by heavy metals [J]. Ecology and Environment , 2006, l5(6): 1204-1208. |
| [19] | Fan J L, Hu Z Y, Ziadi N, et al. Excessive sulfur supply reduces cadmium accumulation in brown rice(Oryza sativa L.) [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2010,158: 409-415. |
| [20] | Li P, Wang X X, Zhang T L, et al. Effects of several amendments on rice growth and uptake of copper and cadmium from a contaminated soil [J]. J ournal of Environmental Sciences, 2008, 20: 449-455. |
| [21] | 刘昭兵, 纪雄辉, 彭 华, 等. 不同类型钙化合物对污染土壤水稻吸收累积 Cd Pb 的影响及机理[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2010, 29 (1) :78-84. LIU Zhao-bing, JI Xiong-hui, PENG Hua, et al. Ef fects of calcium compounds on uptake and accumulation of Cd and Pb by rice and its mechanism in polluted soils[J]. J ournal of Agro-Environment Science , 2010, 29(1) :78-84. |
| [22] | 刘昭兵, 纪雄辉, 王国祥, 等. 赤泥对 Cd 污染稻田水稻生长及吸收累积Cd的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2010, 29(4): 692-697. Liu Zhao-bing, Ji Xiong-hui, Wang Guo-xiang et al. Effects of redmud on rice growth and cadmium uptake in cadmium polluted soil [J]. Journal of A gro-Env ironment Science , 2010, 29(4): 692-697. |
| [23] | 张良运, 李恋卿, 潘根兴, 等.磷、 锌肥处理对降低污染稻田水稻籽 粒 Cd 含量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2009, 18(3) :909-913. Zhang Liang-yun, Li Lian-qing, Pan Gen-xing, et al. Effects of phosphorus and foliar zinc fertilizers on reducing grain Cd concentration of rice grown in a polluted paddy[J]. Ecology and Environmnet, 2009, 18 (3) :909-913. |
| [24] | MohamedA J, Chen J H, Zhen F R, et al. Effect of different N fertilizer forms on antioxidant capacity and grain yield of rice growing under Cd stress[J]. J ournal of Hazardous Materials , 2009, 162:1081-1085. |
| [25] | Du Q, Chen M X, Zhou R, et al. Cd Toxicity and accumulation in rice plants vary with soil nitrogen status and their genotypic difference can be partly attributed to nitrogen uptake capacity[J]. Rice Scie nce, 2009, 16(4) : 283-291. |
| [26] | 滕 斌,李之林,肖立中,等. 施氨水平对优质稻产量、品质及稻米Hg、As、Cd含量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2011,27(7) :30-33. Teng Bin, Li Zhi-lin, Xiao Li-zhong, et al. Effects of nitrogen application level on yield, quality,and Hg,As,Cd concentrations in grains of high quality rice[J]. Chines e A gricultural Science Bulle tin, 2011, 27(7) : 30-33. |
| [27] | 葛 滢,黄丹丹,周权锁. 添加有机物料对淹水土壤Cd活性的影响机制 [J]. 中国环境科学,2009,29(10) :1093-1099. Ge ying, Huang Dan-dan, Zhou Quan-suo, et al. Influence of organic material addition on the variation of Cd activity in submerged soils [J]. China Environme ntal Science , 2009, 29(10) :1093-1099. |
| [28] | 高 山, 陈建斌, 王 果. 有机物料对稻作与非稻作土壤外源镉形态的影响研究 [J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2004, 12(1) :95-98. Gao Shan, Chen Jian-bin, Wang Guo. Effects of organic matter on the forms of added Cd and its dynamic transformation in soil with or with out growth of rice[J]. Chines e J ournal of Eco-Agric ulture, 2004, 12(1) : 95-98. |
| [29] | Liu C P, Li F B, LuoC L, et al. Foliar application of two silica sols reduced cadmium accumulation in rice grains [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials , 2009, 161 : 1466-1472. |
| [30] | WuU L, Lin D Y, SuD C. The effect of planting oilseed rape and compost application on heavy metal forms in soil and Cd and Pb uptake in rice[J]. A gricultural Scie nces in China, 2011,10(2) :267-274. |
| [31] | 王凯荣, 张玉烛,胡荣桂.不同土壤改良剂对降低重金属污染土壤 上水稻糙米铅镉含量的作用[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2007, 26(2): 476-481. Wang Kai-rong, Zhang Yu-zhu, Hu Rong-gui. Effects of different types of soil amelioration materials on reducing concentrations of Pb and Cd in brown rice in heavy metal polluted paddy soils[J]. Journal of A gro-Environme nt Science, 2007, 26(2): 476-481. |
| [32] | Xu W H, Li Y R, He J P, et al. Cd uptake in rice cultivars treated with organic acids and EDTA[J]. J ournal of Environmental Sciences , 2010, 22(3) : 441-447 |
| [33] | 丁凌云,蓝崇钰,林建平,等.不同改良剂对重金属污染农田水稻产量和重金属吸收的影响[J]. 生态环境, 2006, l5(6) :1204-1208. Ding Ling-yun, Lan Chong-yu, Lin Jian-ping, et al. Effects of different ameliorations on rice production and heavy metals uptake by rice grown on soil contaminated by heavy metals [J]. Ecology and Environment , 2006, 15(6) :1204-1208. |
| [34] | 龚海军,刘昭兵,纪雄辉,等. 新型土壤改良剂对水稻吸收累积 Cd、Pb的影响初探[J]. 湖南农业科学, 2010,5: 50-53. Gong Hai-jun, Liu Zhao-bing, Ji Xiong-hui, et al. Effect of new soil amendment on absorption and accumulation of Cd and Pb by rice [J]. Hunan A gricultural Sciences, 2010,5: 50-53. |
| [35] | 周启星, 宋玉芳. 污染土壤修复原理与方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004. Zhou Qi-xing, Song Yu-fang. Principal and method of remediating contaminated soil [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2004. |
| [36] | 仲维功, 杨 杰, 陈志德, 等. 水稻品种及其器官对土壤重金属元素 Pb、 Cd、 Hg、 As 积累的差异[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2006, 22(4): 331-338. Zhong Wei-gong, Yang Jie , Chen Zhi-de, et al. Differences in accumulation and rice cultivars and their organs distribution of Pb, Cd, Hg and As in(Oryza sativa L.) [J]. J iangsu J ournal of A gricultural Sciences, 2006, 22(4): 331-338. |
| [37] | Chen F, Dong J, Wang F, et al. Identification of barley genotypes with low grain Cd accumulation and its interaction with four microelements[J]. Chemos p here , 2007, 67: 2082-2088. |
| [38] | Grant C A, Clarke J M, Duguid S, et al. Selection and breeding of plant cultivars to minimize cadmium accumulation [J]. Scienc e of the Total Environment, 2008, 390(2-3) : 301-310. |
| [39] | 李正文, 张艳玲, 潘根兴, 等. 不同水稻品种籽粒 Cd、Cu和Se的含 量差异及其人类膳食摄取风险 [J].环境科学,2003,24(3) :112-115. Li Zheng-wen, Zhang Yan-ling, Pan Gen-xing, et al. Grain contents of Cd, Cu and Se by 57 rice cultivars and the risk significance for human dietary uptake[J]. Environmental Science, 2003, 24(3) :112-115. |
| [40] | 曾 翔, 张玉烛, 王凯荣, 等. 不同品种水稻糙米含镉量差异[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2006,22(1): 67-69, 83. Zeng Xiang, Zhang Yu-zhu, Wang Kai-rong, et al. Genotype diference of brown rices in Cd Content [J] . J ournal of Ecology and Rural Envi ronment, 2006, 22(1): 67-69, 83. |
| [41] | 程旺大, 张国平, 姚海根, 等. 晚粳稻籽粒中 As、 Cd、 Cr、 Ni、 Pb 等重 金属含量的基因型与环境效应及其稳定性[J].作物学报, 2006, 32 (4) :573-579. Cheng Wang-da, Zhang Guo-ping, Yao Hai-gen, et al. Genotypic and environmental variation and their stability of As, Cr, Cd, Ni and Pb concentrations in the grains of Japonica rice[J ]. ACTA A gronomica Sinica, 2006, 32(4) :573-579. |
| [42] | Yu H, Wang J L, Fang Wei, et al. Cadmium accumulation in different rice cultivars and screening for pollution-safe cultivars of rice[J]. Scie nce of the Total Environme nt, 2006,370: 302-309. |
| [43] | 陈志德, 仲维功, 杨 杰, 等. 不同水稻品种在 Cd、 As 和 Hg 胁迫下 的吸收积累特性[J]. 中国农学通报, 2008, 24(2) :389-393. Chen Zhi-de, Zhong Wei-gong, Yang Jie, et al. Response characteristics of difierent rice cultivars under Cd, As and Hg stress [J]. Chine se A gricultural Science Bulle tin, 2008, 24(2) :389-393. |
| [44] | 成颜君, 龚伟群, 李恋卿, 等.2种杂交水稻对2种不同土壤中Cd吸收与分配的比较 [J].农业环境科学学报,2008, 27(5): 1895-1900. Cheng Yan-jun, Gong Wei-qun, Li Lian-qing, et al. Comparison of Cd uptake and partitioning in plant tissues by two hybrid rice grown in two contrasting paddy soils[J]. J ournal of Agro-Environme nt Sc ience, 2008, 27(5): 1895-1900. |
| [45] | Zeng F R, Mao Y, Cheng W, et al. Genotypic and environmental variation in chromium, cadmium and lead concentrations in rice[J]. Environme ntal Pollution, 2008,153: 309-314. |
| [46] | Shi J, Li L Q, PanG X. Variation of grain Cd and Zn concentrations of 110 hybrid rice cultivars grown in a low-Cd paddy soil [J]. J ournal of Environmental Sciences, 2009,21: 168-172. |
| [47] | 殷敬峰,李华兴,卢维盛,等. 不同品种水稻糙米对 Cd Cu Zn 积累特 性的研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2010, 29(5): 844-851. Yin Jing-feng, Li Hua-xing, Lu Wei-sheng, et al. Variations of Cd, Cu, Zn accumulation among rice cultivars[J]. J ournal of A gro-Environment Science, 2010, 29(5): 844-851. |
| [48] | 刘侯俊, 梁吉哲, 韩晓日,等. 东北地区不同水稻品种对 Cd 的累积特性研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2011,30(2): 220-227. Liu Hou-jun, Liang Ji-zhe, Han Xiao-ri, et al. Accumulation and distribution of cadmium in different rice cultivars of Northeastern China[J]. J ournal of A gro-Environment Science, 2011,30(2): 220-227. |
| [49] | Clarke J M, Depauw RM, Thiessen L L. Registration of five pairs of durum wheat genetic stocks near: Isogenic for cadmium concentration[J]. Crop Science, 1997, 37: 297. |
| [50] | Clarke J M, Norvell W A, Clarke FR, et al. Concentration of cadmium and other elements in the grain of near-isogenoc durum lines[J]. Canadian J ournal of A nimal Sc ience, 2002, 82: 27-33. |
 2012, Vol. 31
2012, Vol. 31